0207 205 2845 0207 205 2845


All antidepressants advise avoiding alcohol, but how dangerous is mixing the two? There are several risks to mixing antidepressants and alcohol. The drugs may not work, worsen side effects or cause dangerous changes to your central nervous system.
Even though the WHO estimates more than 30 million people struggle with depression worldwide, very little is known about the condition.
The same goes for the main form of treatment, antidepressants. Many studies, scans and theories exist about why and how they work, but so much is still uncertain.
We know that alcohol affects the signals in the brain that cause happiness, pleasure, and reward. The short-term effects are positive, but the long-term impact damages this mood-altering part of our mind.
Mixing alcohol and antidepressants is taking two unknowns and putting them together. The result can be acceptable, and it is very moderate alcohol use in most cases.
The catch is that so much is left to chance. You could react badly and make your depression worse. Depression is a harrowing and protracted struggle for most. It doesn’t seem worth the setback for a drink or two.

Despite their name, antidepressants are not just used to treat depression. Anxiety is a common reason for taking SSRIs.
Sadly, many people living with anxiety use alcohol to self-medicate. The effect of alcohol on the brain’s signals gives a temporary calm feeling.
However, the payback the next day is anxiety caused by lowering GABA levels in the body.
Combining antidepressants and alcohol may feel at the time like it lowers your anxiety more. There is a risk of over-depressing your central nervous system. The danger is severe, with some people losing consciousness, breathing issues and insomnia.
There is a range of antidepressants available. For this reason, the dangers of mixing them with alcohol vary. It is essential to know precisely how alcohol reacts with the antidepressant you are taking.
In some cases, alcohol is not recommended. In other cases, it can be dangerous to mix with an antidepressant.
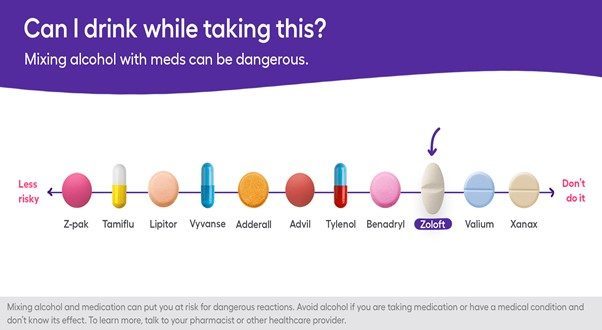
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are the most common antidepressant. These include Sertraline (Zoloft), Citalopram, Fluoxetine and Paroxetine. They stop your brain from taking back serotonin after it is released. This increases serotonin levels in the brain, improving and stabilising your mood.
Alcohol affects serotonin levels, too. The short-term boost of serotonin from alcohol is part of the feel-good experience when drinking.
You probably realise that this doesn’t last long. You may remember feeling great when you start drinking, only to end up emotional, sad, and confused instead.
The next day, you will feel this even more. A hangover is accompanied by low serotonin and dopamine. If you are struggling with a low mood, generally, this will be an even darker time.
There are side effects as well. Mixing alcohol and Sertraline, for example, can increase the typical side effects such as tiredness, lack of coordination and confusion.
Like SSRIs, they encourage higher levels of norepinephrine instead of serotonin. This is another mood-enhancing brain signal. Doctors use it for people who don’t react well to SSRIs and those with significant depression.
These are more dangerous antidepressants to mix with alcohol because they make you drowsy. Alcohol increases this effect, which can be a severe problem.
Combine this with the fact that most people on SNRI medication are more severely depressed, and alcohol doesn’t mix with SNRIs.
This is another antidepressant that makes you feel drowsy. Medications such as Ketamine have an anaesthetic effect. They can help with pain, make you tired, and slow your breathing and heart rate.
Alcohol is a CNS (central nervous system) depressant and does the same. Combining these antidepressants and alcohol increases the effects. This can lead to dangerously low breathing, heart rate and loss of consciousness.
These pills stop your body from reabsorbing serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. This is best for people who have not been successful with milder antidepressants.
Usually, if your depression is resistant to treatment, it is more severe. The worse the depression, the more drinking alcohol with your antidepressants will harm your recovery.
A less common antidepressant, Mirtazapine, has a quicker effect and helps with sleep disorders. Although you can drink on Mirtazapine, it is best to wait a few days to see how it feels first. It can make you feel sleepy and unsteady. If it does, you should avoid alcohol as it will worsen the effect.
One of the oldest types of antidepressants, Tricyclics like Amitriptyline, are less common because you can overdose on them. While you can drink alcohol on this medication, the chances of drowsiness and other dangerous effects are high. You can become unconscious, and breathing depression is made worse by combining the two.

Antidepressants can treat many mental health disorders. Doctors prescribe them for depression, anxiety, PTSD, OCD, and panic attacks.
The link between mental health issues and alcohol addiction and abuse is strong. Over half of those getting rehab treatment in the UK have an underlying mental health problem.
This is no coincidence. Self-medicating with alcohol is disturbingly common. Think of expressions like ‘Dutch courage’ and ‘drowning your sorrows’.
If you have a mental health problem to the extent you take antidepressants, it may be worth avoiding alcohol just for this reason.
The downward cycle can be feeling anxious or depressed, drinking to numb it and then getting worse from the alcohol, needing more alcohol, and so on. If you are struggling with alcohol and find you cannot stop drinking, rehab can help you wrestle back control and prevent your depression from worsening.
Despite their popularity, doctors are still unsure about antidepressants. Studies of the brains of depressed people on antidepressants show that many brain areas are still deficient or shrunk. This may suggest that they are little more than a temporary lifebelt.
More and more, the medical profession suggests natural treatment for depression and anxiety. These have fewer physical side effects than antidepressants, but still, they often don’t go together.

There is a lot of support for exercise in treating depression and anxiety. Some theories even suggest that not exercising can contribute to these conditions. The most effective way to rebuild the damage to the hippocampus is exercise.
Alcohol and exercise don’t go well together. You are less likely to get going if you feel hungover and tired. Dehydration and poor sleep also make exercise less tempting. You might be less able to perform as well, which is discouraging.
Social anxiety can make alcohol feel like a helpful tool for spending time with others. Isolation can lead to anxiety and depression. The problem is that socialising with drinking is rarely the meaningful and supportive interaction that helps with mental health problems.

One of the best antidepressants is talking therapy. Exploring your thoughts, feelings and behaviour patterns through CBT (Cognitive Behaviour Therapy) can significantly improve mood.
Going through intense emotions and sometimes trauma does not mix well with alcohol. More than a drink or two can leave you feeling vulnerable and emotional.
You can ask your counsellor if they think you should avoid drinking for a while.
The relationship between addiction and mental health is firm. Sometimes, alcohol abuse leads to depression, anxiety, and trauma. It also happens the other way people use alcohol to self-medicate for mental health conditions.
Mixing two negative things is not a good idea.
On the upside, antidepressants are an excellent replacement for self-medicating with alcohol. Detox doctors often prescribe them to treat mental health issues during rehab treatment.
Given the challenges of mental health conditions and alcohol, it is best to put your happiness first and give up alcohol while on antidepressants.
If you find you cannot stop drinking alcohol despite wanting to, you may have an alcohol addiction. We can help you diagnose and treat alcohol addiction in a professional medical setting.
GET HELP TODAY. 24 Hour Helpline: 0207 2052845